Portal:Mathematics
- አማርኛ
- العربية
- Avañe'ẽ
- Авар
- تۆرکجه
- বাংলা
- 閩南語 / Bân-lâm-gú
- Беларуская (тарашкевіца)
- Bikol Central
- Български
- Català
- Cebuano
- Čeština
- الدارجة
- Deutsch
- Eesti
- Ελληνικά
- Español
- فارسی
- Français
- Gĩkũyũ
- 한국어
- Hausa
- Հայերեն
- हिन्दी
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Interlingua
- Íslenska
- Italiano
- עברית
- ქართული
- Қазақша
- Kiswahili
- Kreyòl ayisyen
- Kurdî
- Latina
- Lietuvių
- Magyar
- Македонски
- Malti
- مصرى
- ဘာသာမန်
- Bahasa Melayu
- မြန်မာဘာသာ
- Nederlands
- 日本語
- Oʻzbekcha / ўзбекча
- ਪੰਜਾਬੀ
- پښتو
- Picard
- Polski
- Português
- Română
- Runa Simi
- Русский
- Shqip
- සිංහල
- سنڌي
- Slovenčina
- Soomaaliga
- کوردی
- Српски / srpski
- Suomi
- Svenska
- தமிழ்
- Taclḥit
- Татарча / tatarça
- ၽႃႇသႃႇတႆး
- ไทย
- Тоҷикӣ
- Türkçe
- Українська
- اردو
- Tiếng Việt
- 文言
- 吴语
- ייִדיש
- Yorùbá
- 粵語
- Zazaki
- 中文
- Batak Mandailing
- ⵜⴰⵎⴰⵣⵉⵖⵜ ⵜⴰⵏⴰⵡⴰⵢⵜ
Tools
Actions
General
Print/export
In other projects
Appearance
Portal maintenance status: (December 2018)
|
Wikipedia portal for content related to Mathematics
-
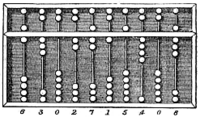
Abacus, a ancient hand-operated calculating.
-
Portrait of Emmy Noether, around 1900.
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, theories and theorems that are developed and proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). (Full article...)
Featured articles – load new batch
-
Image 1

The manipulations of the Rubik's Cube form the Rubik's Cube group.
In mathematics, a group is a set with an operation that associates an element of the set to every pair of elements of the set (as does every binary operation) and satisfies the following constraints: the operation is associative, it has an identity element, and every element of the set has an inverse element.
Many mathematical structures are groups endowed with other properties. For example, the integers with the addition operation form an infinite group, which is generated by a single element called (these properties characterize the integers in a unique way). (Full article...)
-
Image 2
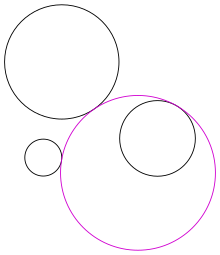
Figure 1: A solution (in purple) to Apollonius's problem. The given circles are shown in black.
In Euclidean plane geometry, Apollonius's problem is to construct circles that are tangent to three given circles in a plane (Figure 1). Apollonius of Perga (c. 262 BC – c. 190 BC) posed and solved this famous problem in his work Ἐπαφαί (Epaphaí, "Tangencies"); this work has been lost, but a 4th-century AD report of his results by Pappus of Alexandria has survived. Three given circles generically have eight different circles that are tangent to them (Figure 2), a pair of solutions for each way to divide the three given circles in two subsets (there are 4 ways to divide a set of cardinality 3 in 2 parts).
In the 16th century, Adriaan van Roomen solved the problem using intersecting hyperbolas, but this solution does not use only straightedge and compass constructions. François Viète found such a solution by exploiting limiting cases: any of the three given circles can be shrunk to zero radius (a point) or expanded to infinite radius (a line). Viète's approach, which uses simpler limiting cases to solve more complicated ones, is considered a plausible reconstruction of Apollonius' method. The method of van Roomen was simplified by Isaac Newton, who showed that Apollonius' problem is equivalent to finding a position from the differences of its distances to three known points. This has applications in navigation and positioning systems such as LORAN. (Full article...) -
Image 3

Logic studies valid forms of inference like modus ponens.
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the study of deductively valid inferences or logical truths. It examines how conclusions follow from premises based on the structure of arguments alone, independent of their topic and content. Informal logic is associated with informal fallacies, critical thinking, and argumentation theory. Informal logic examines arguments expressed in natural language whereas formal logic uses formal language. When used as a countable noun, the term "a logic" refers to a specific logical formal system that articulates a proof system. Logic plays a central role in many fields, such as philosophy, mathematics, computer science, and linguistics.
Logic studies arguments, which consist of a set of premises that leads to a conclusion. An example is the argument from the premises "it's Sunday" and "if it's Sunday then I don't have to work" leading to the conclusion "I don't have to work". Premises and conclusions express propositions or claims that can be true or false. An important feature of propositions is their internal structure. For example, complex propositions are made up of simpler propositions linked by logical vocabulary like(and) or
(if...then). Simple propositions also have parts, like "Sunday" or "work" in the example. The truth of a proposition usually depends on the meanings of all of its parts. However, this is not the case for logically true propositions. They are true only because of their logical structure independent of the specific meanings of the individual parts. (Full article...)
-
Image 4

High-precision test of general relativity by the Cassini space probe (artist's impression): radio signals sent between the Earth and the probe (green wave) are delayed by the warping of spacetime (blue lines) due to the Sun's mass.
General relativity is a theory of gravitation developed by Albert Einstein between 1907 and 1915. The theory of general relativity says that the observed gravitational effect between masses results from their warping of spacetime.
By the beginning of the 20th century, Newton's law of universal gravitation had been accepted for more than two hundred years as a valid description of the gravitational force between masses. In Newton's model, gravity is the result of an attractive force between massive objects. Although even Newton was troubled by the unknown nature of that force, the basic framework was extremely successful at describing motion. (Full article...) -
Image 5

Josiah Willard Gibbs (/ɡɪbz/; February 11, 1839 – April 28, 1903) was an American scientist who made significant theoretical contributions to physics, chemistry, and mathematics. His work on the applications of thermodynamics was instrumental in transforming physical chemistry into a rigorous deductive science. Together with James Clerk Maxwell and Ludwig Boltzmann, he created statistical mechanics (a term that he coined), explaining the laws of thermodynamics as consequences of the statistical properties of ensembles of the possible states of a physical system composed of many particles. Gibbs also worked on the application of Maxwell's equations to problems in physical optics. As a mathematician, he created modern vector calculus (independently of the British scientist Oliver Heaviside, who carried out similar work during the same period) and described the Gibbs phenomenon in the theory of Fourier analysis.
In 1863, Yale University awarded Gibbs the first American doctorate in engineering. After a three-year sojourn in Europe, Gibbs spent the rest of his career at Yale, where he was a professor of mathematical physics from 1871 until his death in 1903. Working in relative isolation, he became the earliest theoretical scientist in the United States to earn an international reputation and was praised by Albert Einstein as "the greatest mind in American history". In 1901, Gibbs received what was then considered the highest honor awarded by the international scientific community, the Copley Medal of the Royal Society of London, "for his contributions to mathematical physics". (Full article...) -
Image 6Elementary algebra studies which values solve equations formed using arithmetical operations.
Algebra is the branch of mathematics that studies certain abstract systems, known as algebraic structures, and the manipulation of expressions within those systems. It is a generalization of arithmetic that introduces variables and algebraic operations other than the standard arithmetic operations, such as addition and multiplication.
Elementary algebra is the main form of algebra taught in schools. It examines mathematical statements using variables for unspecified values and seeks to determine for which values the statements are true. To do so, it uses different methods of transforming equations to isolate variables. Linear algebra is a closely related field that investigates linear equations and combinations of them called systems of linear equations. It provides methods to find the values that solve all equations in the system at the same time, and to study the set of these solutions. (Full article...) -
Image 7In classical mechanics, the Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector (LRL vector) is a vector used chiefly to describe the shape and orientation of the orbit of one astronomical body around another, such as a binary star or a planet revolving around a star. For two bodies interacting by Newtonian gravity, the LRL vector is a constant of motion, meaning that it is the same no matter where it is calculated on the orbit; equivalently, the LRL vector is said to be conserved. More generally, the LRL vector is conserved in all problems in which two bodies interact by a central force that varies as the inverse square of the distance between them; such problems are called Kepler problems.
The hydrogen atom is a Kepler problem, since it comprises two charged particles interacting by Coulomb's law of electrostatics, another inverse-square central force. The LRL vector was essential in the first quantum mechanical derivation of the spectrum of the hydrogen atom, before the development of the Schrödinger equation. However, this approach is rarely used today. (Full article...) -
Image 8

Émile Michel Hyacinthe Lemoine (French: [emil ləmwan]; 22 November 1840 – 21 February 1912) was a French civil engineer and a mathematician, a geometer in particular. He was educated at a variety of institutions, including the Prytanée National Militaire and, most notably, the École Polytechnique. Lemoine taught as a private tutor for a short period after his graduation from the latter school.
Lemoine is best known for his proof of the existence of the Lemoine point (or the symmedian point) of a triangle. Other mathematical work includes a system he called Géométrographie and a method which related algebraic expressions to geometric objects. He has been called a co-founder of modern triangle geometry, as many of its characteristics are present in his work. (Full article...) -
Image 9In algebraic geometry and theoretical physics, mirror symmetry is a relationship between geometric objects called Calabi–Yau manifolds. The term refers to a situation where two Calabi–Yau manifolds look very different geometrically but are nevertheless equivalent when employed as extra dimensions of string theory.
Early cases of mirror symmetry were discovered by physicists. Mathematicians became interested in this relationship around 1990 when Philip Candelas, Xenia de la Ossa, Paul Green, and Linda Parkes showed that it could be used as a tool in enumerative geometry, a branch of mathematics concerned with counting the number of solutions to geometric questions. Candelas and his collaborators showed that mirror symmetry could be used to count rational curves on a Calabi–Yau manifold, thus solving a longstanding problem. Although the original approach to mirror symmetry was based on physical ideas that were not understood in a mathematically precise way, some of its mathematical predictions have since been proven rigorously. (Full article...) -
Image 10
Theodore John Kaczynski (/kəˈzɪnski/ ⓘ kə-ZIN-skee; May 22, 1942 – June 10, 2023), also known as the Unabomber (/ˈjuːnəbɒmər/ ⓘ YOO-nə-bom-ər), was an American mathematician and domestic terrorist. He was a mathematics prodigy, but abandoned his academic career in 1969 to pursue a reclusive primitive lifestyle.
Kaczynski murdered three people and injured 23 others between 1978 and 1995 in a nationwide mail bombing campaign against people he believed to be advancing modern technology and the destruction of the natural environment. He authored Industrial Society and Its Future, a 35,000-word manifesto and social critique opposing all forms of technology, rejecting leftism, and advocating a nature-centered form of anarchism. (Full article...) -
Image 11One of Molyneux's celestial globes, which is displayed in Middle Temple Library – from the frontispiece of the Hakluyt Society's 1889 reprint of A Learned Treatise of Globes, both Cœlestiall and Terrestriall, one of the English editions of Robert Hues' Latin work Tractatus de Globis (1594)
Emery Molyneux (/ˈɛməri ˈmɒlɪnoʊ/ EM-ər-ee MOL-in-oh; died June 1598) was an English Elizabethan maker of globes, mathematical instruments and ordnance. His terrestrial and celestial globes, first published in 1592, were the first to be made in England and the first to be made by an Englishman.
Molyneux was known as a mathematician and maker of mathematical instruments such as compasses and hourglasses. He became acquainted with many prominent men of the day, including the writer Richard Hakluyt and the mathematicians Robert Hues and Edward Wright. He also knew the explorers Thomas Cavendish, Francis Drake, Walter Raleigh and John Davis. Davis probably introduced Molyneux to his own patron, the London merchant William Sanderson, who largely financed the construction of the globes. When completed, the globes were presented to Elizabeth I. Larger globes were acquired by royalty, noblemen and academic institutions, while smaller ones were purchased as practical navigation aids for sailors and students. The globes were the first to be made in such a way that they were unaffected by the humidity at sea, and they came into general use on ships. (Full article...) -
Image 12
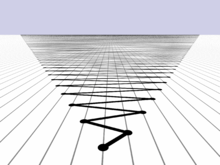
The first 15,000 partial sums of 0 + 1 − 2 + 3 − 4 + ... The graph is situated with positive integers to the right and negative integers to the left.
In mathematics, 1 − 2 + 3 − 4 + ··· is an infinite series whose terms are the successive positive integers, given alternating signs. Using sigma summation notation the sum of the first m terms of the series can be expressed as
The infinite series diverges, meaning that its sequence of partial sums, (1, −1, 2, −2, 3, ...), does not tend towards any finite limit. Nonetheless, in the mid-18th century, Leonhard Euler wrote what he admitted to be a paradoxical equation:(Full article...)
-
Image 13
Georg Ferdinand Ludwig Philipp Cantor (/ˈkæntɔːr/ KAN-tor; German: [ˈɡeːɔʁk ˈfɛʁdinant ˈluːtvɪç ˈfiːlɪp ˈkantoːɐ̯]; 3 March [O.S. 19 February] 1845 – 6 January 1918) was a mathematician who played a pivotal role in the creation of set theory, which has become a fundamental theory in mathematics. Cantor established the importance of one-to-one correspondence between the members of two sets, defined infinite and well-ordered sets, and proved that the real numbers are more numerous than the natural numbers. Cantor's method of proof of this theorem implies the existence of an infinity of infinities. He defined the cardinal and ordinal numbers and their arithmetic. Cantor's work is of great philosophical interest, a fact he was well aware of.
Originally, Cantor's theory of transfinite numbers was regarded as counter-intuitive – even shocking. This caused it to encounter resistance from mathematical contemporaries such as Leopold Kronecker and Henri Poincaré and later from Hermann Weyl and L. E. J. Brouwer, while Ludwig Wittgenstein raised philosophical objections; see Controversy over Cantor's theory. Cantor, a devout Lutheran Christian, believed the theory had been communicated to him by God. Some Christian theologians (particularly neo-Scholastics) saw Cantor's work as a challenge to the uniqueness of the absolute infinity in the nature of God – on one occasion equating the theory of transfinite numbers with pantheism – a proposition that Cantor vigorously rejected. Not all theologians were against Cantor's theory; prominent neo-scholastic philosopher Constantin Gutberlet was in favor of it and Cardinal Johann Baptist Franzelin accepted it as a valid theory (after Cantor made some important clarifications). (Full article...) -
Image 14A stamp of Zhang Heng issued by China Post in 1955
Zhang Heng (Chinese: 張衡; AD 78–139), formerly romanized Chang Heng, was a Chinese polymathic scientist and statesman who lived during the Eastern Han dynasty. Educated in the capital cities of Luoyang and Chang'an, he achieved success as an astronomer, mathematician, seismologist, hydraulic engineer, inventor, geographer, cartographer, ethnographer, artist, poet, philosopher, politician, and literary scholar.
Zhang Heng began his career as a minor civil servant in Nanyang. Eventually, he became Chief Astronomer, Prefect of the Majors for Official Carriages, and then Palace Attendant at the imperial court. His uncompromising stance on historical and calendrical issues led to his becoming a controversial figure, preventing him from rising to the status of Grand Historian. His political rivalry with the palace eunuchs during the reign of Emperor Shun (r. 125–144) led to his decision to retire from the central court to serve as an administrator of Hejian Kingdom in present-day Hebei. Zhang returned home to Nanyang for a short time, before being recalled to serve in the capital once more in 138. He died there a year later, in 139. (Full article...) -
Image 15

The weighing pans of this balance scale contain zero objects, divided into two equal groups.
In mathematics, zero is an even number. In other words, its parity—the quality of an integer being even or odd—is even. This can be easily verified based on the definition of "even": zero is an integer multiple of 2, specifically 0 × 2. As a result, zero shares all the properties that characterize even numbers: for example, 0 is neighbored on both sides by odd numbers, any decimal integer has the same parity as its last digit—so, since 10 is even, 0 will be even, and if y is even then y + x has the same parity as x—indeed, 0 + x and x always have the same parity.
Zero also fits into the patterns formed by other even numbers. The parity rules of arithmetic, such as even − even = even, require 0 to be even. Zero is the additive identity element of the group of even integers, and it is the starting case from which other even natural numbers are recursively defined. Applications of this recursion from graph theory to computational geometry rely on zero being even. Not only is 0 divisible by 2, it is divisible by every power of 2, which is relevant to the binary numeral system used by computers. In this sense, 0 is the "most even" number of all. (Full article...)
Good articles – load new batch
-
Image 1
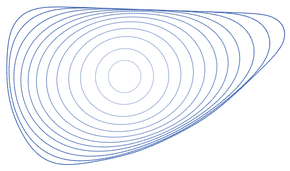
Convergence of a convex curve to a circle under the curve-shortening flow. Inner curves (lighter color) are flowed versions of the outer curves. Time steps between curves are not uniform.
In mathematics, the curve-shortening flow is a process that modifies a smooth curve in the Euclidean plane by moving its points perpendicularly to the curve at a speed proportional to the curvature. The curve-shortening flow is an example of a geometric flow, and is the one-dimensional case of the mean curvature flow. Other names for the same process include the Euclidean shortening flow, geometric heat flow, and arc length evolution.
As the points of any smooth simple closed curve move in this way, the curve remains simple and smooth. It loses area at a constant rate, and its perimeter decreases as quickly as possible for any continuous curve evolution. If the curve is non-convex, its total absolute curvature decreases monotonically, until it becomes convex. Once convex, the isoperimetric ratio of the curve decreases as the curve converges to a circular shape, before collapsing to a singularity. If two disjoint simple smooth closed curves evolve, they remain disjoint until one of them collapses to a point. (Full article...) -
Image 2
In graph theory, a branch of mathematics, the Herschel graph is a bipartite undirected graph with 11 vertices and 18 edges. It is a polyhedral graph (the graph of a convex polyhedron), and is the smallest polyhedral graph that does not have a Hamiltonian cycle, a cycle passing through all its vertices. It is named after British astronomer Alexander Stewart Herschel, because of Herschel's studies of Hamiltonian cycles in polyhedral graphs (but not of this graph). (Full article...) -
Image 3
Schwarz lantern on display in the German Museum of Technology, Berlin
In mathematics, the Schwarz lantern is a polyhedral approximation to a cylinder, used as a pathological example of the difficulty of defining the area of a smooth (curved) surface as the limit of the areas of polyhedra. It is formed by stacked rings of isosceles triangles, arranged within each ring in the same pattern as an antiprism. The resulting shape can be folded from paper, and is named after mathematician Hermann Schwarz and for its resemblance to a cylindrical paper lantern. It is also known as Schwarz's boot, Schwarz's polyhedron, or the Chinese lantern.
As Schwarz showed, for the surface area of a polyhedron to converge to the surface area of a curved surface, it is not sufficient to simply increase the number of rings and the number of isosceles triangles per ring. Depending on the relation of the number of rings to the number of triangles per ring, the area of the lantern can converge to the area of the cylinder, to a limit arbitrarily larger than the area of the cylinder, or to infinity—in other words, the area can diverge. The Schwarz lantern demonstrates that sampling a curved surface by close-together points and connecting them by small triangles is inadequate to ensure an accurate approximation of area, in contrast to the accurate approximation of arc length by inscribed polygonal chains. (Full article...) -
Image 4
Eugene Paul Wigner (Hungarian: Wigner Jenő Pál, pronounced [ˈviɡnɛr ˈjɛnøː ˈpaːl]; November 17, 1902 – January 1, 1995) was a Hungarian-American theoretical physicist who also contributed to mathematical physics. He received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1963 "for his contributions to the theory of the atomic nucleus and the elementary particles, particularly through the discovery and application of fundamental symmetry principles".
A graduate of the Technical Hochschule Berlin (now Technische Universität Berlin), Wigner worked as an assistant to Karl Weissenberg and Richard Becker at the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute in Berlin, and David Hilbert at the University of Göttingen. Wigner and Hermann Weyl were responsible for introducing group theory into physics, particularly the theory of symmetry in physics. Along the way he performed ground-breaking work in pure mathematics, in which he authored a number of mathematical theorems. In particular, Wigner's theorem is a cornerstone in the mathematical formulation of quantum mechanics. He is also known for his research into the structure of the atomic nucleus. In 1930, Princeton University recruited Wigner, along with John von Neumann, and he moved to the United States, where he obtained citizenship in 1937. (Full article...) -
Image 5

In mathematics, a binary operation is commutative if changing the order of the operands does not change the result. It is a fundamental property of many binary operations, and many mathematical proofs depend on it. Perhaps most familiar as a property of arithmetic, e.g. "3 + 4 = 4 + 3" or "2 × 5 = 5 × 2", the property can also be used in more advanced settings. The name is needed because there are operations, such as division and subtraction, that do not have it (for example, "3 − 5 ≠ 5 − 3"); such operations are not commutative, and so are referred to as noncommutative operations. The idea that simple operations, such as the multiplication and addition of numbers, are commutative was for many years implicitly assumed. Thus, this property was not named until the 19th century, when mathematics started to become formalized. A similar property exists for binary relations; a binary relation is said to be symmetric if the relation applies regardless of the order of its operands; for example, equality is symmetric as two equal mathematical objects are equal regardless of their order. (Full article...) -
Image 6

A spiral staircase in the Cathedral of St. John the Divine. Several helical curves in the staircase project to hyperbolic spirals in its photograph.
A hyperbolic spiral is a type of spiral with a pitch angle that increases with distance from its center, unlike the constant angles of logarithmic spirals or decreasing angles of Archimedean spirals. As this curve widens, it approaches an asymptotic line. It can be found in the view up a spiral staircase and the starting arrangement of certain footraces, and is used to model spiral galaxies and architectural volutes.
As a plane curve, a hyperbolic spiral can be described in polar coordinatesby the equation
for an arbitrary choice of the scale factor(Full article...)
-
Image 7The infinity symbol (∞) is a mathematical symbol representing the concept of infinity. This symbol is also called a lemniscate, after the lemniscate curves of a similar shape studied in algebraic geometry, or "lazy eight", in the terminology of livestock branding.
This symbol was first used mathematically by John Wallis in the 17th century, although it has a longer history of other uses. In mathematics, it often refers to infinite processes (potential infinity) rather than infinite values (actual infinity). It has other related technical meanings, such as the use of long-lasting paper in bookbinding, and has been used for its symbolic value of the infinite in modern mysticism and literature. It is a common element of graphic design, for instance in corporate logos as well as in older designs such as the Métis flag. (Full article...) -
Image 8

A set of 20 points in a 10 × 10 grid, with no three points in a line.
The no-three-in-line problem in discrete geometry asks how many points can be placed in thegrid so that no three points lie on the same line. The problem concerns lines of all slopes, not only those aligned with the grid. It was introduced by Henry Dudeney in 1900. Brass, Moser, and Pach call it "one of the oldest and most extensively studied geometric questions concerning lattice points".
At mostpoints can be placed, because
points in a grid would include a row of three or more points, by the pigeonhole principle. Although the problem can be solved with
points for every
up to
, it is conjectured that fewer than
points can be placed in grids of large size. Known methods can place linearly many points in grids of arbitrary size, but the best of these methods place slightly fewer than
points, not
. (Full article...)
-
Image 9
A tessellation or tiling is the covering of a surface, often a plane, using one or more geometric shapes, called tiles, with no overlaps and no gaps. In mathematics, tessellation can be generalized to higher dimensions and a variety of geometries.
A periodic tiling has a repeating pattern. Some special kinds include regular tilings with regular polygonal tiles all of the same shape, and semiregular tilings with regular tiles of more than one shape and with every corner identically arranged. The patterns formed by periodic tilings can be categorized into 17 wallpaper groups. A tiling that lacks a repeating pattern is called "non-periodic". An aperiodic tiling uses a small set of tile shapes that cannot form a repeating pattern (an aperiodic set of prototiles). A tessellation of space, also known as a space filling or honeycomb, can be defined in the geometry of higher dimensions. (Full article...) -
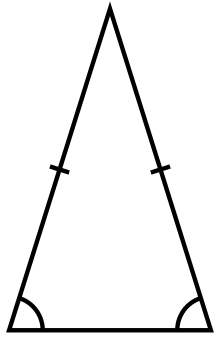
Image 10
In geometry, an isosceles triangle (/aɪˈsɒsəliːz/) is a triangle that has two sides of equal length or two angles of equal measure. Sometimes it is specified as having exactly two sides of equal length, and sometimes as having at least two sides of equal length, the latter version thus including the equilateral triangle as a special case.
Examples of isosceles triangles include the isosceles right triangle, the golden triangle, and the faces of bipyramids and certain Catalan solids.
The mathematical study of isosceles triangles dates back to ancient Egyptian mathematics and Babylonian mathematics. Isosceles triangles have been used as decoration from even earlier times, and appear frequently in architecture and design, for instance in the pediments and gables of buildings. (Full article...) -
Image 11The Euclid–Euler theorem is a theorem in number theory that relates perfect numbers to Mersenne primes. It states that an even number is perfect if and only if it has the form 2p−1(2p − 1), where 2p − 1 is a prime number. The theorem is named after mathematicians Euclid and Leonhard Euler, who respectively proved the "if" and "only if" aspects of the theorem.
It has been conjectured that there are infinitely many Mersenne primes. Although the truth of this conjecture remains unknown, it is equivalent, by the Euclid–Euler theorem, to the conjecture that there are infinitely many even perfect numbers. However, it is also unknown whether there exists even a single odd perfect number. (Full article...) -
Image 12
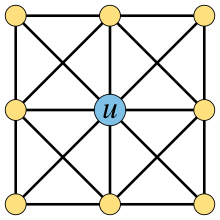
A graph with a universal vertex, u
In graph theory, a universal vertex is a vertex of an undirected graph that is adjacent to all other vertices of the graph. It may also be called a dominating vertex, as it forms a one-element dominating set in the graph. A graph that contains a universal vertex may be called a cone, and its universal vertex may be called the apex of the cone. This terminology should be distinguished from the unrelated usage of these words for universal quantifiers in the logic of graphs, and for apex graphs.
Graphs that contain a universal vertex include the stars, trivially perfect graphs, and friendship graphs. For wheel graphs (the graphs of pyramids), and graphs of higher-dimensional pyramidal polytopes, the vertex at the apex of the pyramid is universal. When a graph contains a universal vertex, it is a cop-win graph, and almost all cop-win graphs contain a universal vertex. (Full article...)
Did you know (auto-generated) – load new batch

- ... that the British National Hospital Service Reserve trained volunteers to carry out first aid in the aftermath of a nuclear or chemical attack?
- ... that The Math Myth advocates for American high schools to stop requiring advanced algebra?
- ... that Latvian-Soviet artist Karlis Johansons exhibited a skeletal tensegrity form of the Schönhardt polyhedron seven years before Erich Schönhardt's 1928 paper on its mathematics?
- ... that despite a mathematical model deeming the ice cream bar flavour Goody Goody Gum Drops impossible, it was still created?
- ... that in the aftermath of the American Civil War, the only Black-led organization providing teachers to formerly enslaved people was the African Civilization Society?
- ... that the discovery of Descartes' theorem in geometry came from a too-difficult mathematics problem posed to a princess?
- ... that Green Day's "Wake Me Up When September Ends" became closely associated with the aftermath of Hurricane Katrina?
- ... that people in Madagascar perform algebra on tree seeds in order to tell the future?
More did you know – view different entries

- ...that it is impossible to devise a single formula involving only polynomials and radicals for solving an arbitrary quintic equation?
- ...that Euler found 59 more amicable numbers while for 2000 years, only 3 pairs had been found before him?
- ...that you cannot knot strings in 4 dimensions, but you can knot 2-dimensional surfaces, such as spheres?
- ...that there are 6 unsolved mathematics problems whose solutions will earn you one million US dollars each?
- ...that there are different sizes of infinite sets in set theory? More precisely, not all infinite cardinal numbers are equal?
- ...that every natural number can be written as the sum of four squares?
- ...that the largest known prime number is nearly 41 million digits long?
Showing 7 items out of 75
Featured pictures
-
Image 1Mandelbrot set, step 4, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 2Hypotrochoid, by Sam Derbyshire (edited by Anevrisme and Perhelion) (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 3Mandelbrot set, step 6, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 4Fields Medal, front, by Stefan Zachow (edited by King of Hearts) (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 5Mandelbrot set, step 5, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 7Proof of the Pythagorean theorem, by Joaquim Alves Gaspar (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 8Tetrahedral group at Symmetry group, by Debivort (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 10Mandelbrot set, step 10, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 12Mandelbrot set, step 14, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 14Cellular automata at Reflector (cellular automaton), by Simpsons contributor (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 15Mandelbrot set, step 11, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 16Mandelbrot set, by Simpsons contributor (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 17Line integral of scalar field, by Lucas V. Barbosa (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 19Mandelbrot set, step 3, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 20Fields Medal, back, by Stefan Zachow (edited by King of Hearts) (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 23Mandelbrot set, step 8, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 24Mandelbrot set, step 7, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
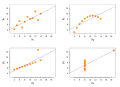
Image 25Anscombe's quartet, by Schutz (edited by Avenue) (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 26Mandelbrot set, step 2, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 27Desargues' theorem, by Dynablast (edited by Jujutacular and Julia W) (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 28Non-uniform rational B-spline, by Greg L (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 29Mandelbrot set, step 1, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 30Mandelbrot set, step 12, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 31Mandelbrot set, start, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 32Mandelbrot set, step 13, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 33Lorenz attractor at Chaos theory, by Wikimol (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
-
Image 34Mandelbrot set, step 9, by Wolfgangbeyer (from Wikipedia:Featured pictures/Sciences/Mathematics)
Get involved
- For editor resources and to collaborate with other editors on improving Wikipedia's Mathematics-related articles, visit WikiProject Mathematics.
Categories
Topics
Index of articles
| ARTICLE INDEX: | |
| MATHEMATICIANS: |
Vital articles
- » subpages: Level 4 Mathematics articles, Level 5 Mathematics articles
Discover Wikipedia using portals
Hidden categories:
- Pages with French IPA
- Pages using the Phonos extension
- Pages including recorded pronunciations
- Pages with German IPA
- Pages with Hungarian IPA
- Wikipedia semi-protected portals
- Manually maintained portal pages from December 2018
- All manually maintained portal pages
- Portals with triaged subpages from December 2018
- All portals with triaged subpages
- Portals with named maintainer
- Wikipedia move-protected portals
- Automated article-slideshow portals with 31–40 articles in article list
- Automated article-slideshow portals with 101–200 articles in article list
- Random portal component with over 50 available subpages